Customizing DNS Service
This page explains how to configure your DNS Pod and customize the DNS resolution process. In Kubernetes version 1.11 and later, CoreDNS is at GA and is installed by default with kubeadm. See Configuring CoreDNS and Using CoreDNS for Service Discovery.
- Before you begin
- Introduction
- Inheriting DNS from the node
- Configure stub-domain and upstream DNS servers
- ConfigMap options
- Configuring CoreDNS
- CoreDNS ConfigMap options
- Migration to CoreDNS
- What’s next
Before you begin
You need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using Minikube, or you can use one of these Kubernetes playgrounds:
To check the version, enter kubectl version.
- Kubernetes version 1.6 or later. To work with CoreDNS, version 1.9 or later.
- The appropriate add-on: kube-dns or CoreDNS. To install with kubeadm, see the kubeadm reference documentation.
Introduction
DNS is a built-in Kubernetes service launched automatically using the addon manager cluster add-on.
The running DNS Pod holds 3 containers:
- “
kubedns“: watches the Kubernetes master for changes in Services and Endpoints, and maintains in-memory lookup structures to serve DNS requests. - “
dnsmasq“: adds DNS caching to improve performance. - “
sidecar“: provides a single health check endpoint to perform healthchecks fordnsmasqandkubedns.
The DNS Pod is exposed as a Kubernetes Service with a static IP.
The kubelet passes DNS to each container with the --cluster-dns=<dns-service-ip>
flag.
DNS names also need domains. You configure the local domain in the kubelet
with the flag --cluster-domain=<default-local-domain>.
The Kubernetes cluster DNS server is based on the SkyDNS library. It supports forward lookups (A records), service lookups (SRV records), and reverse IP address lookups (PTR records).
Inheriting DNS from the node
When running a Pod, kubelet prepends the cluster DNS server and searches paths to the node’s DNS settings. If the node is able to resolve DNS names specific to the larger environment, Pods should also be able to resolve. But see Known issues.
If you don’t want this, or if you want a different DNS config for pods, you can
use the kubelet’s --resolv-conf flag. Set this flag to “” to prevent Pods from
inheriting DNS. Set it to a valid file path to specify a file other than
/etc/resolv.conf for DNS inheritance.
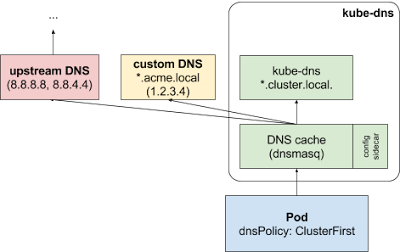
Configure stub-domain and upstream DNS servers
Cluster administrators can specify custom stub domains and upstream nameservers
by providing a ConfigMap for kube-dns (kube-system:kube-dns).
For example, the following ConfigMap sets up a DNS configuration with a single stub domain and two upstream nameservers:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: kube-dns
namespace: kube-system
data:
stubDomains: |
{"acme.local": ["1.2.3.4"]}
upstreamNameservers: |
["8.8.8.8", "8.8.4.4"]DNS requests with the “.acme.local” suffix are forwarded to a DNS listening at 1.2.3.4. Google Public DNS serves the upstream queries.
The table below describes how queries with certain domain names map to their destination DNS servers:
| Domain name | Server answering the query |
|---|---|
| kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local | kube-dns |
| foo.acme.local | custom DNS (1.2.3.4) |
| widget.com | upstream DNS (one of 8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4) |
See ConfigMap options for details about the configuration option format.
Effects on Pods
Custom upstream nameservers and stub domains do not affect Pods with a
dnsPolicy set to “Default” or “None”.
If a Pod’s dnsPolicy is set to “ClusterFirst”, its name resolution is
handled differently, depending on whether stub-domain and upstream DNS servers
are configured.
Without custom configurations: Any query that does not match the configured cluster domain suffix, such as “www.kubernetes.io”, is forwarded to the upstream nameserver inherited from the node.
With custom configurations: If stub domains and upstream DNS servers are configured, DNS queries are routed according to the following flow:
The query is first sent to the DNS caching layer in kube-dns.
From the caching layer, the suffix of the request is examined and then forwarded to the appropriate DNS, based on the following cases:
Names with the cluster suffix, for example “.cluster.local”: The request is sent to kube-dns.
Names with the stub domain suffix, for example “.acme.local”: The request is sent to the configured custom DNS resolver, listening for example at 1.2.3.4.
Names without a matching suffix, for example “widget.com”: The request is forwarded to the upstream DNS, for example Google public DNS servers at 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4.
ConfigMap options
Options for the kube-dns kube-system:kube-dns ConfigMap:
| Field | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
stubDomains (optional) |
A JSON map using a DNS suffix key such as “acme.local”, and a value consisting of a JSON array of DNS IPs. | The target nameserver can itself be a Kubernetes Service. For instance, you can run your own copy of dnsmasq to export custom DNS names into the ClusterDNS namespace. |
upstreamNameservers (optional) |
A JSON array of DNS IPs. | If specified, the values replace the nameservers taken by default from the node’s /etc/resolv.conf. Limits: a maximum of three upstream nameservers can be specified. |
Examples
Example: Stub domain
In this example, the user has a Consul DNS service discovery system they want to
integrate with kube-dns. The consul domain server is located at 10.150.0.1, and
all consul names have the suffix .consul.local. To configure Kubernetes, the
cluster administrator creates the following ConfigMap:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: kube-dns
namespace: kube-system
data:
stubDomains: |
{"consul.local": ["10.150.0.1"]}Note that the cluster administrator does not want to override the node’s
upstream nameservers, so they did not specify the optional
upstreamNameservers field.
Example: Upstream nameserver
In this example the cluster administrator wants to explicitly force all
non-cluster DNS lookups to go through their own nameserver at 172.16.0.1.
In this case, they create a ConfigMap with the
upstreamNameservers field specifying the desired nameserver:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: kube-dns
namespace: kube-system
data:
upstreamNameservers: |
["172.16.0.1"]Configuring CoreDNS
You can configure CoreDNS as a service discovery.
CoreDNS is available as an option in Kubernetes starting with version 1.9. It is currently a GA feature and is on course to be the default, replacing kube-dns.
CoreDNS ConfigMap options
CoreDNS chains plugins and can be configured by maintaining a Corefile with the ConfigMap. CoreDNS supports all the functionalities and more that is provided by kube-dns.
A ConfigMap created for kube-dns to support StubDomainsand upstreamNameservers translates to the proxy plugin in CoreDNS.
Similarly, the Federation plugin translates to the federation plugin in CoreDNS.
Example
This example ConfigMap for kubedns specifies federations, stubdomains and upstreamnameservers:
apiVersion: v1
data:
federations: |
{"foo" : "foo.feddomain.com"}
stubDomains: |
{"abc.com" : ["1.2.3.4"], "my.cluster.local" : ["2.3.4.5"]}
upstreamNameservers: |
["8.8.8.8", "8.8.4.4"]
kind: ConfigMapThe equivalent configuration in CoreDNS creates a Corefile:
For federations:
federation cluster.local { foo foo.feddomain.com }For stubDomains:
abc.com:53 { errors cache 30 proxy . 1.2.3.4 } my.cluster.local:53 { errors cache 30 proxy . 2.3.4.5 }
The complete Corefile with the default plugins:
.:53 {
errors
health
kubernetes cluster.local in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa {
upstream 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4
pods insecure
fallthrough in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa
}
federation cluster.local {
foo foo.feddomain.com
}
prometheus :9153
proxy . 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4
cache 30
}
abc.com:53 {
errors
cache 30
proxy . 1.2.3.4
}
my.cluster.local:53 {
errors
cache 30
proxy . 2.3.4.5
}In Kubernetes version 1.10 and later, kubeadm supports automatic translation of the CoreDNS ConfigMap from the kube-dns ConfigMap.
Migration to CoreDNS
A number of tools support the installation of CoreDNS instead of kube-dns. To migrate from kube-dns to CoreDNS, a detailed blog is available to help users adapt CoreDNS in place of kube-dns.